 Malaysia
Malaysia
|
| Basic Facts |
| Country name |
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Malaysia local long form: none local short form: Malaysia former: Federation of Malaysia |
| Gevernment type | constitutional monarchy
note: nominally headed by paramount ruler and a bicameral Parliament consisting of a nonelected upper house and an elected lower house; all Peninsular Malaysian states have hereditary rulers except Melaka and Pulau Pinang (Penang); those two states along with Sabah and Sarawak in East Malaysia have governors appointed by government; powers of state governments are limited by federal constitution; under terms of federation, Sabah and Sarawak retain certain constitutional prerogatives (e.g., right to maintain their own immigration controls); Sabah holds 25 seats in House of Representatives; Sarawak holds 28 seats in House of Representatives |
| Capital |
name: Kuala Lumpur
geographic coordinates: 3 10 N, 101 42 E time difference: UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) note: Putrajaya is referred to as administrative center not capital; Parliament meets in Kuala Lumpur |
| Flag description | 14 equal horizontal stripes of red (top) alternating with white (bottom); there is a blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing a yellow crescent and a yellow 14-pointed star; the crescent and the star are traditional symbols of Islam; the design was based on the flag of the US |
| Currency | ringgit (MYR) |
| Internet country code | .my |
| Ports and terminals | Bintulu, Johor, Labuan, Lahad Datu, Lumut, Miri, George Town (Penang), Port Kelang, Tanjung Pelepas |
| Agriculture products | Peninsular Malaysia - rubber, palm oil, cocoa, rice; Sabah - subsistence crops, rubber, timber, coconuts, rice; Sarawak - rubber, pepper, timber |
| Industries | Peninsular Malaysia - rubber and oil palm processing and manufacturing, light manufacturing industry, electronics, tin mining and smelting, logging, timber processing; Sabah - logging, petroleum production; Sarawak - agriculture processing, petroleum production and refining, logging |
| Geography |
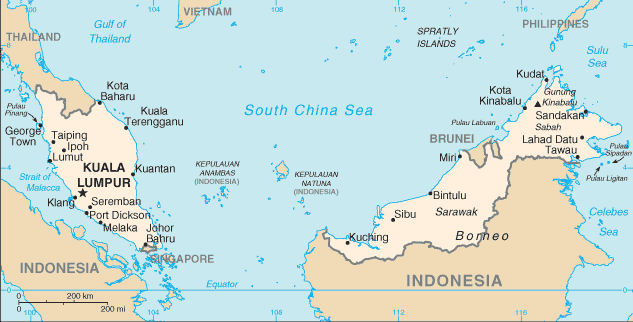
| Location | Southeastern Asia, peninsula bordering Thailand and northern one-third of the island of Borneo, bordering Indonesia, Brunei, and the South China Sea, south of Vietnam |
| Coordinates | 2 30 N, 112 30 E |
| Continent | Southeast Asia |
| Area |
total: 329,750 sq km
land: 328,550 sq km water: 1,200 sq km |
| Boundaries |
total: 2,669 km
border countries: Brunei 381 km, Indonesia 1,782 km, Thailand 506 km |
| Coastline | 4,675 km (Peninsular Malaysia 2,068 km, East Malaysia 2,607 km) |
| Climate | tropical; annual southwest (April to October) and northeast (October to February) monsoons |
| Terrain | coastal plains rising to hills and mountains |
| Natural resources | tin, petroleum, timber, copper, iron ore, natural gas, bauxite |
| Natural hazards | flooding, landslides, forest fires |
| People |
| Population | 24,385,858 (July 2006 est.) |
| Ethnic groups | Malay 50.4%, Chinese 23.7%, Indigenous 11%, Indian 7.1%, others 7.8% (2004 est.) |
| Religions | Muslim, Buddhist, Daoist, Hindu, Christian, Sikh; note - in addition, Shamanism is practiced in East Malaysia |
| Languages | Bahasa Melayu (official), English, Chinese (Cantonese, Mandarin, Hokkien, Hakka, Hainan, Foochow), Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, Panjabi, Thai
note: in East Malaysia there are several indigenous languages; most widely spoken are Iban and Kadazan |

